1. Introduction:
In terms of section 68 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 (hereinafter referred as CGST Act) read with rule 138 of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Rules 2017 (here in after referred as CGST Rule), E-Way Bill is a document to be carried by the person in charge of conveyance along with the goods and need to be generated electronically from the E-Way Bill Portal. The objective is quick and easy movement of goods across India without any hindrance.
2. Effective date of applicability of E-Way Bill
| Particulars |
Effective date |
| Inter-state movement of Goods |
|
| For all the states and union territories |
1st April, 2018 |
| Intra-state movement of goods |
|
| For Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Kerala, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh |
15th April, 2018 |
| For Bihar, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Tripura and Uttarakhand |
20th April, 2018 |
| For Arunachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Meghalaya, Pondicherry and Sikkim |
25th April, 2018 |
| For Nagaland |
1stMay, 2018 |
| For Rajasthan |
20th May, 2018 |
| For Maharashtra, Andaman & Nicobar, Chandigarh, Dadara & Nagar Haveli, Daman & Diu, Lakshadweep and Manipur |
25th May, 2018 |
| For Chhattisgarh, Goa, Jammu & Kashmir, Odisha, Punjab and Mizoram |
1st June, 2018 |
| For Delhi |
16th June, 2018 |
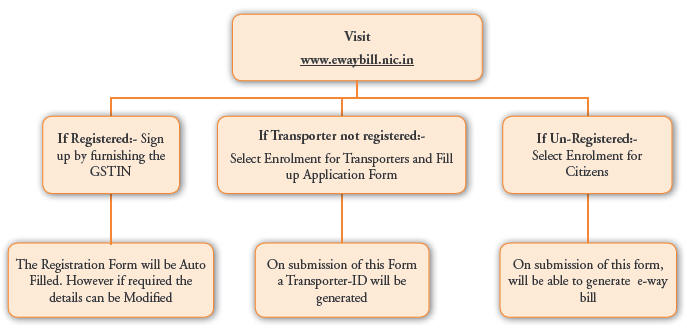
3. Registration on the E-Way Bill system
The registration mechanism for the GST taxpayers for the e-Way Bill system is a simple process. The GST registered person can register on the e-way bill portal by visiting at www.ewaybill.nic.in and create his user credentials to use the system. GST registered person can be a supplier, recipient, transporter, e-commerce operator or courier agency. In case the transporter is small operator and not registered under the GST, then this system provides the mechanism to enroll and create his user credentials to operate on this system.
Note: If the Registered person transport the good in his own/hired vehicle, such person need not to be registered as a transporter.
4. Various way to generate E-Way bill :-
♦ Using web base system
♦ Using SMS base facility
♦ Using Android App
♦ Bulk generation facility
♦ Using site to site integration facility
♦ Using Goods and Service Tax suvidha provider
5. When should e-way bill be issued?[Rule138(1)]
5.1. Registered person who causes movement of goods of consignment value exceeding ₹ 50000/- shall generate E-way bill—
a. in relation to a supply (Sale, Transfer, supply to distinct person, Related person, Principal to agent or vice versa, etc.); or
b. for reasons other than supply (For demo, repairing, Job work, one branch to another branch within the state, etc.); or
c. due to inward supply from an unregistered person.
5.2. E-Way bill shall be generated through form EWB-01. This form has Two Parts as "PART A" this contains information w.r.t. Goods in movement and "Part B" which contains details of Vehicle and/or Transporter. E-Way bill will be generated only after filling Part A and Part B both. Its needs to be generated before commencement of such movement and a unique number will be generated on the said portal.
5.3. If goods to be transported are supplied through an E-Commerce Operator or a courier agency, on an authorization received from the consignor, the information in Part A of EWB-01 may be furnished by such E-commerce Operator or Courier Agency.
5.4. For following specified Goods, the e-way bill needs to be generated mandatorily even if the value of the consignment of Goods is less than ₹ 50,000: Proviso to [Rule 138(1)]
♦ Where goods are sent for job work by a principal located in one State or Union territory to a job worker located in any other State or Union territory.
♦ Where handicraft goods are transported from one State or Union territory to another State or Union territory by a person who has been exempted from the requirement of obtaining registration.
5.5. To check the applicability of the E-Way bill, consignment value is to be determined as per Section 15 of CGST Act and includes GST applicable. It means it is the value of the goods declared in invoice, a bill of supply or a delivery challan as the case may be, issued in respect of the said consignment and also include Central tax, State or Union territory tax, Integrated tax and Cess charged, if any. But, it will exclude the value of exempt supply of goods, where the invoice is issued in respect of both exempt and taxable supply.
5.6. Value of material in case of job work and leasing: In case of material sent for job work, the value should be total value of goods, when goods are returned after job work, the value should be inclusive of value of goods.
In case of equipment sent for leasing, value of equipment should be full value and not merely leasing charges.
6. Who is liable to issue E-Way bill [Rule 138(1), (2), (2A), (3)]
| Transaction |
Recipient |
Supplier |
Transportation mode |
Transporter |
EWB-01 Part A |
EWB-01 Part B |
| Intra/Inter state |
Registered/Unregistered |
Registered |
By road through a transporter |
Registered |
Person who is causing movement |
See note 1 below* |
| Intra/Inter State |
Registered/unregistered |
Registered |
By Road, through a Transporter |
Unregistered |
As Above |
See note 1 below* |
| Intra/Inter State |
Registered/unregistered |
Registered |
By Hired or Owned Vehicle or through Public Conveyance |
- |
Registered Person - who hired or owned vehicle for transportation Or - who is making movement of goods |
Same as Part A |
| Intra/Inter State |
Registered/unregistered |
Registered |
By Air/Train/Vessel |
- |
Registered Person who is making movement |
Same as Part A |
| Intra State |
Registered |
Unregistered |
By Road, through a Transporter |
Registered |
Registered Recipient |
See Note 1 Below* |
| Intra State |
Registered |
Unregistered |
By Road, through a Transporter |
Unregistered |
As Above |
As Above |
| Intra State |
Registered |
Unregistered |
By Hired/Owned Vehicle/Public Conveyance |
- |
Registered Recipient |
Registered Recipient |
| Intra State |
Registered |
Unregistered |
By Air/Train/Vessel |
- |
Registered Recipient |
Registered Recipient |
*Note 1: Filling of Part B is important as without Part B filling EWB No. cannot be generated. First responsibility to fill Part B also lies with the person who has filled Part A. However as provided in sub-rule (3), if person filling Part A has not provided with details of vehicle which will finally carry the consignment, he can mention the GSTIN of Registered Transporter or Transporter ID of Unregistered Transporter. In that case transporter has to provide details of vehicle in Part B and finally has to generate EWB No.
7. Important points to be noted
7.1. However Rule 138(1), (2), (3) cast first liability of E-Way Bill on registered person who causes movement (as explained above in table), it may be noted that in case both registered party (supplier and recipient), practically E-Way bill can be generated by any one of them.
7.2. Sub-rule (2A) creates specific liability of registered person to generate e-way bill in case goods are transported by railways or by air or vessel. In case of railways or by air or vessel, detail in Part B of E-way bill can be furnished after the movements of goods begin. In case of Railway, E-way bill required to be furnished at the time of delivery of goods.
7.3. First Proviso of Rule 138(3) provides an option to Registered Person or the Transporter to generate the E-way Bill even if value of consignment is < ₹ 50,000.
7.4. Third Proviso of rule 138(3) and (5) provides relaxation for not to furnish details of conveyance in Part B of Form GST EWB-01, if the goods are transported for a distance of upto fifty kilometers within the State or Union territory from the place of business of the consignor to the place of business of the transporter for further transportation or from place of business of the transporter to the place of business of consignee.
7.5. No e-Way bill is required for movement of goods upto a distance of 20 Km from the place of business of consignor to a weighbridge for weighment or from the weighbridge back to the place of business of consignor, within the same State, subject to the condition that the movement of goods is accompanied by a delivery challan issued.
8. Role of Transporter in E Way Bill
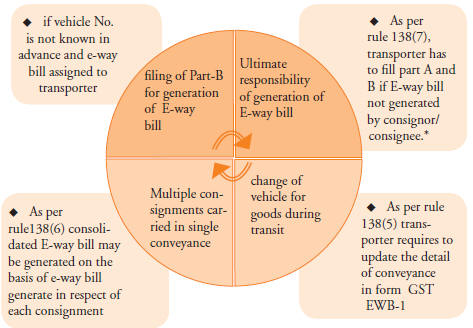
* As per Rule 138(7) Where consignor or consignee has not generated E-way bill and the value of consignment carried in a conveyance exceed ₹ 50,000/-, the transporter in respect of inter-state supply is required to generate E-way bill in FORM GST EWB-01. He can also generate consolidated E-way bill in FORM GST EWB-02. However this provision is not applicable if goods are transported by railways, air and vessel.
9. Change of transporter before or during the movement of goods: [Rule 138(5A)]
Subcontracting is very common in transportation where the transporters assignment of load is transferred to another transporter. This sub-rule can be analyzed in two parts -
Before updation of Vehicle details in Part B: E-Way bill can be assigned to another transporter either by person who furnished Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 or Transporter.
After updation of vehicle details in Part B: E-way bill cannot be assigned to another transporter if the details of Part B of FORM GST EWB-01 are furnished by the transporter after furnishing of Part A of FORM GST-EWB-01 by the registered person.
10. E-way bill in case of Transshipment, multimodal transportation:
10.1. Where the consignment of one E-way bill has to be moved in multiple vehicle after moving to transshipment place. For e.g. e-Way Bill is generated and needs to be moved from place A to place C. Here, the consignment moves from A to B via rail or bigger vehicle. Now, it is not possible to move the consignment from B to C in the same mode of transportation due to unavailability of that mode or may be due to hilly region or any other reason where big vehicles cannot be used. In such cases, the consignment needs to be moved in multiple smaller vehicles.
10.2. Steps to be followed:
(i) First generate the e-Way Bill with source and destination as per the document/invoice.
(ii) Carry out the first leg of movement of the Consignment up to the transshipment.
(iii) Choose the 'Change to Multi-vehicle' option and update the e-Way Bill for multi-vehicle movement. Here, the total quantity of the consignment and movement from and to place for the multiple vehicles requirement has to be entered.
(iv) Now, when the consignment has been loaded to the smaller vehicle, update the 'Part-B' of the e-Way Bill with the vehicle number, along with the quantity loaded, and move the consignment.
(v) Step No. (iv) may be repeated till total quantity is loaded and moved. The system will not allow the quantity to be shipped in multiple vehicles more than what has been declared while marking the e-Way Bill for multi-vehicle.
11. Validity period of E-way Bill [Rule-138(10)]
| Time Allowed |
Normal Cargo |
Over Dimensional Cargo* |
| 1 Day |
Upto 100 Km |
Upto 20 Km |
| 1 additional Day |
For every 100 Km or part thereof thereafter |
For every 20 Km or part thereof thereafter |
Note:
♦ Over Dimensional Cargo mean a cargo carried as a single indivisible unit and which exceeds the dimensional limits prescribed in rule 93 of the Central Motor Vehicles Rules 1989 made under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 or [multimodal shipment in which at least one leg involves transport by ship] w.e.f. 28th June, 2019.
♦ Period of validity shall be counted from the date at which the e-way bill has been generated and each day shall be counted as the period expiring at midnight of the day immediately following the date of generation of e-way bill. e.g. E-Way bill generated on June 1, 2019 for a distance of 520 Km, so First 100 Km = 1 Day and for another 400 Km = 4 Day (1 day each for every additional 100 Km) and for balance 20 Km = 1 Day (100 Km or Part thereof). Total validity period is 6 days. Now 1st day will be counted till the midnight of 2nd June. Therefore 6 days validity will end on June 07, 2019.
♦ In case of circumstances of an exceptional nature including transshipment, the goods cannot be transported within the validity period of the e-way bill, the transporter may extend validity period of e-way bill after updating the details in Part B of FORM GSTEWB-01.The validity of the e-way bill may be extended within eight hours from the time of its expiry. Practically period of eight hours is too short because E-way bill expires at 12 midnight and there is no working hours till 8 am.
12. Cancellation of E-Way Bill [Rule 138(9)]: Where an e-way bill has been generated but
♦ Goods are either not transported at all or
♦ Are not transported as per the details furnished in the e-way bill
E-way bill may be cancelled within 24 hours of generation of the E-way bill. However an E-way bill cannot be cancelled if it has been verified in transit in accordance with the provisions of rule 138B.
13. Acceptance or Rejection of E-Way bill [Rule 138(11),(12)]:
13.1. Details of E-way bill generated shall be made to the following person:
♦ supplier, if registered, where the information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 has been furnished by the recipient or the transporter; or
♦ recipient, if registered, where the information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 has been furnished by the supplier or the transporter.
13.2. Either of the party to whom information is made available as per above sub-rule has to communicate his acceptance or rejection within 72 hours of:
♦ details being made available to him on the common portal, or
♦ the time of delivery of goods
Whichever is earlier.
13.3. If such acceptance or rejection has not been communicated within the above specified period, it shall be deemed that he has accepted the said details.
14. E-way bill not required to be generated [Rule 138(14)]
| |
a. |
where the goods being transported are specified in Annexure (Refer Note 1); |
| |
b. |
where the goods are being transported by a non-motorized conveyance; |
| |
c. |
where the goods are being transported from the customs port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station to an inland container depot or a container freight station for clearance by Customs; |
| |
d. |
in respect of movement of goods within such areas as are notified under clause (d) of sub-rule (14) of rule 138 of the State or Union territory Goods and Services Tax Rules in that particular State or Union territory; |
| |
e. |
where the goods, other than de-oiled cake, being transported, are specified in the Schedule appended to notification No. 2/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated the 28th June, 2017. |
| |
f. |
where the goods being transported are alcoholic liquor for human consumption, petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas or aviation turbine fuel; |
| |
g. |
where the supply of goods being transported is treated as no supply under Schedule III of the Act; |
| |
h. |
where the goods are being transported—
(i) under customs bond from an inland container depot or a container freight station to a customs port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station, or from one customs station or customs port to another customs station or customs port, or
(ii) under customs supervision or under customs seal; |
| |
i. |
where the goods being transported are transit cargo from or to Nepal or Bhutan; |
| |
j. |
where the goods being transported are exempt from tax . |
| |
k. |
any movement of goods caused by defence formation under Ministry of defence as a consignor or consignee; |
| |
l. |
where the consignor of goods is the Central Government, Government of any State or a local authority for transport of goods by rail; |
| |
m. |
where empty cargo containers are being transported; and |
| |
n. |
where the goods are being transported upto a distance of twenty kilometers from the place of the business of the consignor to a weighbridge for weighment or from the weighbridge back to the place of the business of the said consignor subject to the condition that the movement of goods is accompanied by a delivery challan . |
| |
o. |
where empty cylinders for packing of liquefied petroleum gas are being moved for reasons other than supply.(Inserted by N/No.26/2018- Central Tax, effective from 13th June, 2018) |
NOTE 1: ANNEXURE [See rule 138(14)]
| |
S. No. |
Description of Goods |
| |
1. |
Liquefied petroleum gas for supply to household and non-domestic exempted category (NDEC) customers |
| |
2. |
Kerosene oil sold under PDS |
| |
3. |
Postal baggage transported by Department of Posts |
| |
4. |
Natural or cultured pearls and precious or semi-precious stones; precious metals and metals clad with precious metal |
| |
5. |
Jewellery, goldsmiths and silversmiths wares and other articles |
| |
6. |
Currency |
| |
7. |
Used personal and household effects |
| |
8. |
Coral, unworked (0508) and worked coral (9601) |
15. Documents and devices to be carried mandatorily by person in charge of conveyance [Rule 138A] read with rule 55A of CGST Rules.
15.1. The person in charge of conveyance shall carry:
♦ The invoice, bill of supply or delivery challan, as the case may be; and
♦ Copy of e-way bill or the e-way bill number, either physically or in electronic form or mapped to a Radio Frequency Identification Device (RFID). If movement of goods is by rail or air or vessel. This clause shall not apply.
♦ In case of imported goods a copy of bill of entry filed by importer.
15.2. Concept of invoice reference number :
♦ A registered person may obtain an Invoice Reference Number from the common portal by uploading, on the said portal, a tax invoice issued by him in FORM GST INV-1 and produce the same for verification by the proper officer in lieu of the tax invoice and such number shall be valid for a period of thirty days from the date of uploading.
♦ This is an additional option given to registered person in case of taxable supply where a Tax invoice is issued. Using this option an IRN can be generated by filing Form GST INV-1 on portal. However after generating, IRN will be valid for 30 days.
♦ Information for E-Way Bill generation under Part A of Form EWB-01 shall be auto populated.
♦ No need to carry physical copy of Tax invoice during transit only IRN will be sufficient.
16. Verification of documents and conveyances [Rule 138B]
16.1. Verification can be carried out by Commissioner or an officer as authorized by the Commissioner in this behalf to intercept any conveyance to verify E-way bill in physical or electronic form for all inter state and intra state movement of goods.
16.2. Radio Frequency Identification Device readers shall be installed at the place of verification of movement of goods. Verification of vehicles shall be done through this device reader where E-way bill has been mapped with the said device.
16.3. The physical verification of conveyances shall be carried out by the proper officer as authorized in this behalf.
17. Inspection and verification of goods[Rule 138C]

♦ A summary report of every inspection of goods in transit shall be recorded online by the proper officer in Part A of FORM GST EWB-03 within twenty four hours of inspection and the final report in Part B of FORM GST EWB-03 shall be recorded within three days of the inspection. Provided that such period of three day may be extended for a further period not exceeding three days on sufficient cause being shown.
Note:
♦ Period of 24 hours or 3 days as the case may be shall be counted from the midnight of the date on which the vehicle was intercepted.
♦ If physical Verification is done during transit at one place within the state or Union territory or in any other State or union territory, no further physical verification can be carried out again in the state or union territory unless in case where evasion of tax is suspected.
♦ If the goods are intercepted or detained for a period exceeding 30 minutes, the transporter may upload the information in FORM GST EWB-04. As the online facility to upload FORM GST EWB-04 is yet to be activated, same can be filed manually also.
18. Procedure to be followed by Proper Officer (Circular No. 41/15/2018-GST dated 13th April, 2018)
18.1. If the transporter fails to provide the documents asked for verification, the proper officer shall follow these steps:
i. Record statement of the transporter in Form GST MOV-01
ii. Issue an order for physical verification/inspection of goods in Form GST MOV-02.
iii. Within 24 hours of issuance of Form GST MOV-02, the proper officer shall prepare a report in Part A of Form GST EWB-03 and upload the same on common portal.
iv. On completion of physical verification/inspection, proper officer shall prepare a report in Form GST MOV-04 and serve a copy of the same to the person in charge of the goods.
v. The final report of inspection shall be recorded by the proper officer in Part B of Form GST EWB-03 within 3 days of such inspection
18.2. If no discrepancies are found after inspection, an order in Form GST MOV-05 shall be passed releasing the vehicle and goods and the vehicle can move on.
18.3. If during the inspection and verification process the officer feels that the goods have to be detained under section 129 of CGST Act, the officer shall take the following action:
♦ Issue order of detention in Form GST MOV-06.
♦ Issue a notice levying the tax and penalty in Form GST MOV-07.
18.4. The proper officer shall release the goods and conveyance by an order in Form GST MOV-05 after the owner of the goods or any person authorized by him has:
♦ Paid the amount of tax and Penalty, or
♦ Furnished a security in form of Bank Guarantee (along with a bond in Form GST MOV-08).
18.5. In case tax and penalty are not paid within 7 Days from the date of issuance of Form GST MOV-06, action under section 130 of CGST Act shall be initiated by serving notice in Form GST MOV-10, proposing confiscation of goods and conveyance and imposition of penalty.
An order for confiscation of goods and conveyance or for imposition of penalty shall be issued in Form GST MOV-11 after giving the person in charge the proper opportunity of being heard and considering the objections filed by him and such order shall be uploaded on the common portal.
18.6. In case no person comes forward to make payment of tax, penalty and fine imposed, within the time specified in Form GST MOV-11, the proper officer shall auction the goods and/or conveyance by public auction and remit the sale proceeds to account of the Central Government.
18.7. A summary of every order in Form GST MOV-09 and Form GST MOV-11 shall be uploaded in Form GST DRC-07 on the common portal.
19. Restriction of furnishing information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 (Rule 138E)
19.1. If a person paying tax under composition scheme has not furnished returns for two consecutive periods and in other cases person has not furnished returns for a consecutive period of two months, they shall not be allowed to furnish information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01.
19.2. The commissioner may allow furnishing of FORM GST EWB-01 if he is satisfied with the reasons given by the aforesaid person in writing.
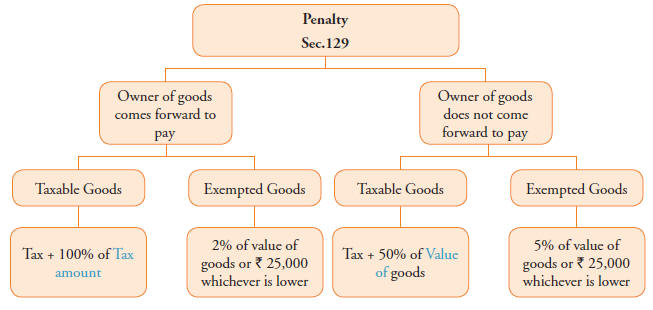
20. Offence and penalty
20.1. Below penal provisions may get attracted for not complying with E-Way bill rules:
♦ Section 122(1) : Where a taxable person who issues any invoice or bill without supply of goods or transports any taxable goods without the cover of documents as may be specified he shall be liable to penalty of ten thousand rupees or an amount equivalent to the tax evaded whichever is higher.
♦ Section 129(1): Where any goods transported or stored in the contravention of provision of this act and rules made thereunder then such goods and conveyance and documents relating to such goods and conveyance shall be liable to detention and seizure and shall be released on payment of taxes and penalties as follow:-
21. Miscellaneous:
21.1. What has to be done by the Transporter if consignee refuses take goods or reject the goods for any reason?
If the consignee or the recipient reject to take delivery of the consignment the transporter can get one more e-way bill generated with the help of the supplier or recipient by indicating supply as 'Sales return' with relevant documents and return the goods to the supplier.
21.2. How to handle Bill to Ship to invoice in E-way bill system?
In case the tax payer raises the bill to one person and sends the consignment to the other person as per the business requirements. There is a provision in the e-way bill system to handle this situation, called as 'Bill to' and 'Ship to'. In the e-way bill form, there are two portions under 'TO' section. In the left hand side - 'Billing To' GSTIN and trade name is entered and in the right hand side -'Ship to' address of the destination of the movement is entered. The other details are entered as per the invoice. In case ship to state is different from Bill to State, the tax components are entered as per the billing state party. That is, if the Bill to location is inter-state for the supplier, IGST is entered and if the Bill to Party location is intra-state for the supplier, the SGST and CGST are entered irrespective of movement of goods whether movement happened within state or outside the state.
21.3. How to handle "Bill From" - "Dispatch From" invoice in E-way bill system?
In case the supplier prepares the bill from his business premises to consignee, but moves the consignment from some other premises to the consignee as per the business requirements. This is known as 'Billing From' and 'Dispatching From'. E-way bill system has provision for this. In the e-way bill form, there are two portions under 'FROM' section. In the left hand side - 'Bill From' supplier's GSTIN and trade name are entered and in the right hand side -'Dispatch From', address of the dispatching place is entered. The other details are entered as per the invoice. In case Bill FROM location State is different from the State of Dispatch the Tax components are entered as per the State (Bill From). That is, if the billing party is inter-state for the supplier, IGST is entered and if the billing party is intra-state for the supplier, the SGST and CGST are entered irrespective of movement of goods whether movement happened within state or outside the state.
21.4. How to generate E-way bill if goods of one invoice is being moved in multiple vehicles simultaneously?
Where the goods are being transported in a semi knocked down (SKD) or completely knocked down (CKD) condition, the EWB shall be generated as follow:
(a) Supplier shall issue the complete invoice before dispatch of the first consignment;
(b) Supplier shall issue a delivery challan for each of the subsequent consignments, giving reference of the invoice;
(c) Each consignment shall be accompanied by copies of the corresponding delivery challan along with a duly certified copy of the invoice; and
(d) Original copy of the invoice shall be sent along with the last consignment.
21.5. How to calculate distance if goods are send for export or received in case of import?
♦ In case of export- From the premises of consignor where the goods are loaded for movement, to the custom port or airport or custom bonded warehouse, where the goods are kept or export clearance.
♦ In case of import- From the custom port or airport or custom bonded warehouse as the case may be, to the premises of consignee.
21.6. How to register on E-way bill Portal if transporter is registered in multiple state or Union territories in GST Portal?
As per Rule 58(1A) of CGST Rules, 2017 for the purpose of e-Way Bill, a transporter registered in multiple States or Union territory having the same PAN number, may apply for a unique common enrolment number by submitting the details in FORM GST ENR-02 using any one of his GSTIN numbers. Where the said transporter has obtained a unique common number, he shall not be eligible to use any of GSTIN numbers for the purpose of said e-Way Bill Rules.
21.7. How to generate E-way bill for multiple invoices belonging to same consignor and consignee?
If multiple invoices are issued by supplier to recipient, for each invoice one E-way bill has to be generated irrespective of the fact that whether same or different consignors or consignees are involved. If goods are going in one vehicle then after generation of all the E-way bills one consolidated E-way bill can be generated for transportation purpose.
21.8. Can provisions of Section 129 be invoked in case of Certain Technical errors?
It has been clarified via Circular 64/38/2018 dated 14th September, 2018 that provisions of Section 129 shall not be applicable if E-way contains following technical errors:
♦ Spelling mistakes in the name of the consignor or the consignee but GSTIN is correct.
♦ Error in pin code but the address of the consignor or the consignee is correct.
♦ Error in address of consignee but locality and other details are correct.
♦ Error in one or two digits of document number mentioned in E-way bill.
♦ Error in one or two digits character of the vehicle number.
♦ Error in 4 or 6 digit level of HSN Code where first 2 digits are correct and rate of tax is correct.
21.9. Enhancements in E-way bill FORM:
♦ Tax payers or transporters can view the list of E-way bills which is about to expire in a period of 4 days. They can keep track of expiry dates for each of the consignments generated.
♦ The taxpayer or transporter can extend the validity of E-way bill in case of the consignment is in Transit/Movement.
♦ Generation of multiple E-way bills based on one invoice shall not be allowed.
♦ For generation of e-way bill distance shall be auto calculated. However user can also enter the distance manually as per the movement of goods but it shall be limited to 10% more than the auto calculated distance displayed.
♦ Transporter ID is compulsory for generating Part A of bill.
♦ In case if invoice value is more than ₹ 10 crore generator of E-way bill a SMS will also be sent to the generator. This will assist him to correct/cancel if it has been entered wrongly.
❑❑